Omics analysis
2022-09-15
Chapter 1 Omics Analysis
多组学整合分析随着高通量技术的广泛应用而生,研究人员可以从基因组、转录组、蛋白质组、交互组、表观基因组、代谢组、脂质体和微生物组等不同分子层面大规模获取组学数据,多组学整合数据分析使得生物学发生了革命性的变化,促进我们对生物过程和分子机制的深刻理解。单一组学分析方法可以提供不同生命进程或者疾病组与正常组相比差异的生物学过程的信息。但是,这些分析往往有局限性。多组学方法整合几个组学水平的信息,为生物机制提供了更多证据,从深层次挖掘候选关键因子;通过将各种组学,不同层面之间信息进行整合,构建基因调控网络,深层次理解各个分子之间的调控及因果关系,从而更深入的认识生物进程和疾病过程中复杂性状的分子机理和遗传基础。
公司常见组学数据类型:微生物组(宏基因组/16S),代谢组,转录组,临床/表型数据等。
Three tools would be introduced in this book:
And the details of the tools are given below.
1.1 Introducution to WGCNA
The WGCNA R software package is a comprehensive collection of R functions for performing various aspects of weighted correlation network analysis. The package includes functions for network construction, module detection, gene selection, calculations of topological properties, data simulation, visualization, and interfacing with external software. Along with the R package we also present R software tutorials. While the methods development was motivated by gene expression data, the underlying data mining approach can be applied to a variety of different settings.

WGCNA workflow
7 steps are included in WGCNA (Detailed in Chapter1):
The Definition of a Gene Co-expression Similarity
The Definition of a Family of Adjacency Functions
Determining the Parameters of the Adjacency Function
Defining a Measure of Node Dissimilarity
Identifying Gene Modules
Relating Network Concepts to Each Other
In the WGCNA chapter, two demo data were used:
16S data from SLE project (45 samples with 1364 ASVs)
MGS and metabolic data from GvHD project (32 samples with 250 species features and 811 metabolite features)
1.2 Introducution to HAllA
HAllA (Hierarchical All-against-All association) 是一个针对多维度、异质型数据集的多重关联分析工具。可用于连续型/分类型数值数据,且在同质型(homogeneous)数据集(所有数值皆相同类型,例如:RNA-seq 基因表現)与异质型(heterogeneous)数据集(不同单位或类型的数值,例如:病患临床指标)皆可高效分析。在目前微生物研究中,HAllA是一個常用于微生物组-代谢、微生物组-临床指标、微生物组-转录组(基因表現、miRNA、GO) 等关联分析的重要工具。

HAllA workflow
Note: Users can use output from WGCNA as input for HALLA.
1.3 Introducution to NetCoMi
Estimating microbial association networks from high-throughput sequencing data is a common exploratory data analysis approach aiming at understanding the complex interplay of microbial communities in their natural habitat. Statistical network estimation workflows comprise several analysis steps, including methods for zero handling, data normalization and computing microbial associations. Since microbial interactions are likely to change between conditions, e.g. between healthy individuals and patients, identifying network differences between groups is often an integral secondary analysis step.
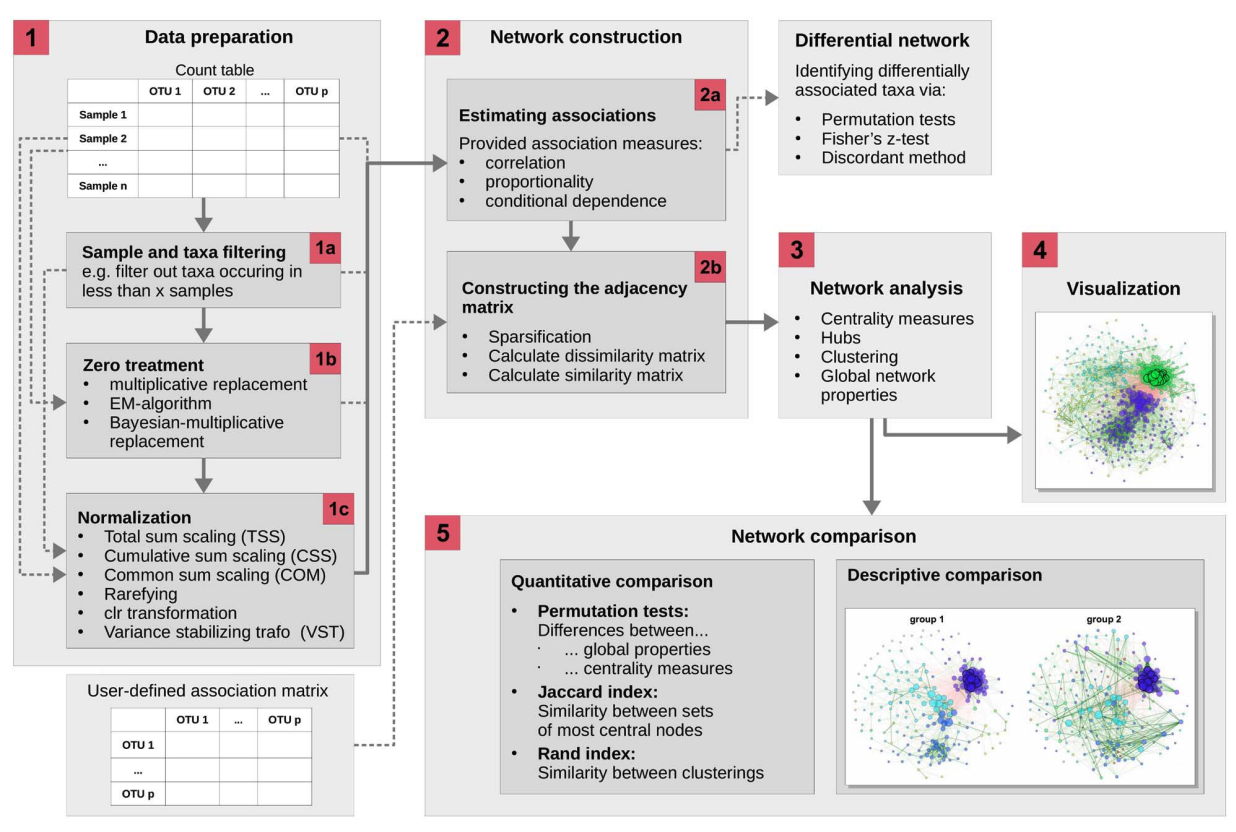
NetCoMi workflow